
Stress maneuvers of the medial collateral ligament, with or without Medial meniscus lesion and osteoarthritis: Pain and sensitivity would be present in the medial compartment, while in the pes anserinus bursitis they are located inferomedial to the medial joint interline.Stress-fracture of the shinbone on the proximedial side will cause pain in the area of the Pes Anserine.Pes Anserine bursitis is often confused with other causes of medial knee pain. Pivoting, kicking, squatting or quick movements from side to side, such as in the sports mentioned above, may also cause further irritation.Aggravating factors include activities that require movements like flexion and endorotation, as well as exorotation and adduction.Postural dysfunction/impaired lower extremity biomechanics.*Other clinical presentations may include: As well, the region around the bursa will be swollen or tender to touch.
 The patient may experience spontaneous anteromedial knee pain on climbing or descending stairs and tenderness at the PA. Pes Anserine bursitis causes pain on the inside of the knee (mostly during running or taking stairs). * Which Are Sign/Symptoms in Pes Anserine Bursitis ? We can say that an inflamed bursa is not a primary pathology, but rather a consequence of an earlier complication. We can explain this by the fact that women have a wider pelvis, resulting in angulation of the knee in the frontal plane, which leads to more pressure in the area of insertion of the pes anserinus by genu valgum. Reports suggest that anserine bursitis is more common in overweight middle-aged females. The bursa then becomes inflamed and tendered or painful and underlying Osteoarthritis of the knee. A contusion to this area results in an increased release of synovial fluid in the lining of the bursa. The bursitis can also be due to a trauma, such as a direct hit in the Pes Anserine region. This causes friction and also increases pressure on the bursa.
The patient may experience spontaneous anteromedial knee pain on climbing or descending stairs and tenderness at the PA. Pes Anserine bursitis causes pain on the inside of the knee (mostly during running or taking stairs). * Which Are Sign/Symptoms in Pes Anserine Bursitis ? We can say that an inflamed bursa is not a primary pathology, but rather a consequence of an earlier complication. We can explain this by the fact that women have a wider pelvis, resulting in angulation of the knee in the frontal plane, which leads to more pressure in the area of insertion of the pes anserinus by genu valgum. Reports suggest that anserine bursitis is more common in overweight middle-aged females. The bursa then becomes inflamed and tendered or painful and underlying Osteoarthritis of the knee. A contusion to this area results in an increased release of synovial fluid in the lining of the bursa. The bursitis can also be due to a trauma, such as a direct hit in the Pes Anserine region. This causes friction and also increases pressure on the bursa. 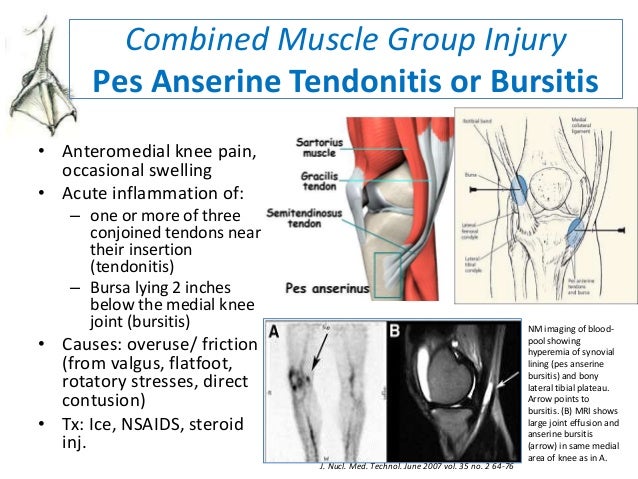
Pes Anserine bursitis often occurs when the related muscles are repeatedly used, by doing movements such as flexion and adduction.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
